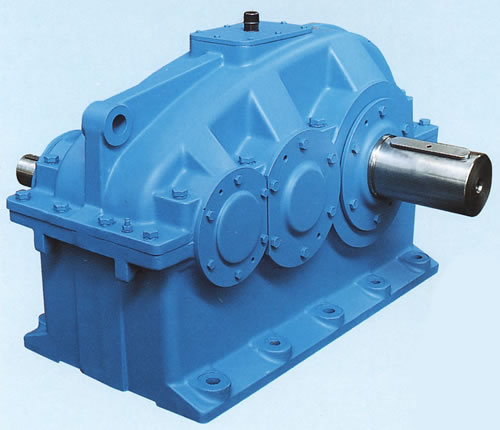
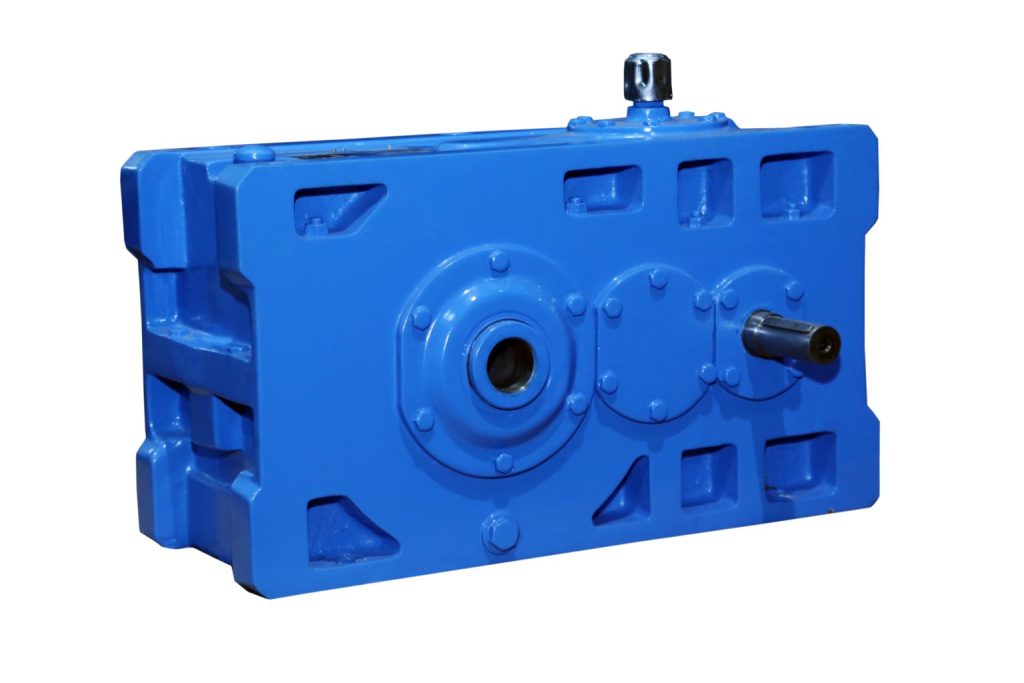
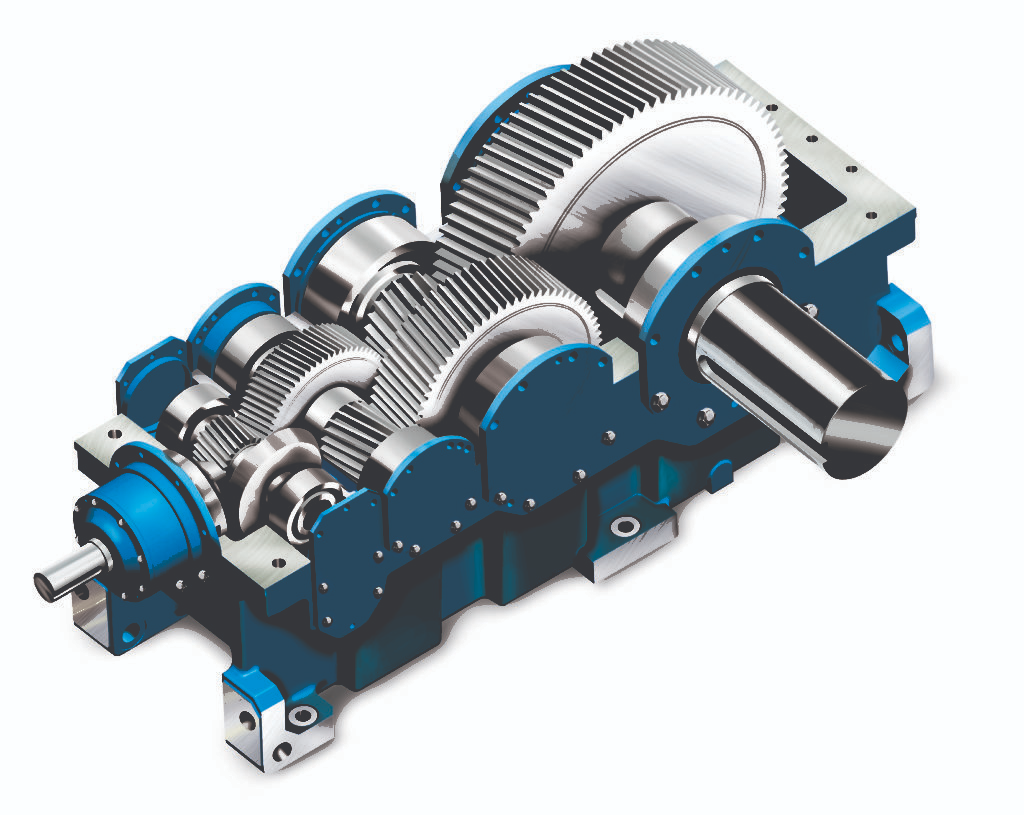
Helical gearboxes are utilized to induce motion and transmit power between two non-crossing shafts. Helical gearboxes are similar to spur gearboxes, however, their teeth are cut over the surface at an angle to the axis of the gear.
These gears can work with each other, both when they are at an angle to each other, also when their axis are parallel. Contingent on load, pressure, and the specific operation, Helical Gearboxes can be made utilizing an assortment of materials, for example, cast iron, steel, metal, copper, plastic, and so forth.
Advantages Of Helical Gearboxes
1) The teeth in helical gears connect inch by inch at a time. It does not connect the whole set at once which takes into account a noiseless activity.
2) At an effective cost, the transmission of energy between parallel shafts likewise permits the control transmission between non-parallel shafts.
3) The teeth in helical gearboxes are bigger in size when compared to those in spur gears, as they are diagonally placed. In this way, for a similar gear size, helical gears can deal with more load comparatively
4) As a result of their remarkable outline at any point of time, the heavy load is conveyed along a set of teeth that are in proximity to each other. It essentially reduces wear and tear. Further, it builds the load-bearing potential and also the working life expectancy of helical gears.
Disadvantages OF Helical Gearboxes:
1) In helical gearboxes, a sliding-type contact is present between the two gears. It results in an undesirable push in the direction of the axial. Furthermore, it prompts more heat because of friction due to sliding. This results in the loss of power transmission, bringing down the effectiveness.
2) For tending to the undesirable axial thrust, a special thrust bearing should be utilized. In order to decrease the friction due to sliding, additives should be mixed with grease. Accordingly, a helical gearbox configuration is more confounded, and the working expense is also more.